- Acid Reflux Disease.
- Ulcer disease ("peptic ulcer") Includes H. Pylori.

Acid Reflux Disease GERD
What is GERD?
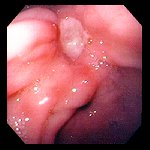
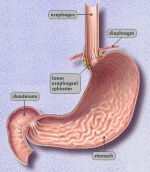
Gastroesophageal reflux disease refers to the abnormal frequency of acid from the stomach washing up the swallowing tube (esophagus) which can lead to the feeling of heartburn or burning in the throat. With time this can lead to erosion (or wearing away) of the swallowing tube (esophageal) lining.How common is it?
Very common and getting more common. An estimated 15 million Americans have chronic GERD. An estimated 7% of the adult population have heartburn daily.What are GERD risk factors?
Age, over 40, being overweight and use of alcohol and coffee add to the risk of GERD.How is GERD different than heartburn?
Just about everyone has heartburn occasionally especially with certain foods like pepperoni pizza or garlicky foods. GERD refers to a disorder where this occurs with abnormal frequency of at least 3 times per week or where there are esophageal erosions. One does not have to have esophageal erosions to have GERD.What should I do if I think I have GERD?
Avoid overeating and avoid those foods you know aggravate the symptoms typically greasy foods, spicy foods and alcohol.See your doctor or GI doctor.
In many cases special testing with EGD endoscopy (a flexible thin scope to look into the esophagus stomach under sedation) is appropriate. Also, other disorders can mimic GERD. Such disorders include stomach ulcers, heart disease and others.
Accurate diagnosis is important.
Why can't I just take Tums, Zantac or Prilosec OTC?
Those medicines will work for GERD, but it is important if symptoms are chronic that you know what your diagnosis is and that a proper evaluation be done. GERD is a chronic condition and getting things right the first time in terms of a treatment plan is important. Simple heartburn can have short term treatment. GERD with erosions in the esophagus usually requires long term maintenance.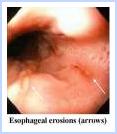
Can GERD be cured?
GERD can be managed so that patients have few if any symptoms.Weight loss and diet changes can reduce GERD. A true cure is less common.
Surgery is needed in rare cases.
The outlook for GERD patients is good with medical therapy.
Ulcer disease ("peptic ulcer") Includes H. Pylori
What are ulcers of the intestinal tract?
Ulcers are sore or breaks in the intestinal lining. They can occurs in various places of the GI tract but most commonly when the word "ulcer" is used regarding the GI tract it refers to the stomach (the organ that holds food after it exits the swallowing tube) or the duodenum (the intestine just after the stomach).